Overview
This article explores the seven stages of Alzheimer’s disease, offering essential caregiving strategies tailored to each stage. Our goal is to enhance the quality of life for both patients and caregivers. Understanding these stages is crucial; it allows caregivers to adapt their approaches effectively. This knowledge not only helps manage the emotional and physical challenges faced but also provides vital support for individuals living with dementia.
As you navigate this journey, remember that you’re not alone. We’re here to help you every step of the way. By recognizing the unique needs at each stage, you can foster a nurturing environment that promotes comfort and dignity. Caregiving can be overwhelming, but with the right strategies, you can make a meaningful difference in the lives of those you care for.
In addition, we encourage you to reach out for support. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide comfort and reassurance. Your well-being is important, and together, we can create a compassionate community that prioritizes care and understanding.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Alzheimer’s disease is a journey that deeply affects not only those diagnosed but also their caregivers. As the leading cause of dementia, this progressive neurological disorder brings unique challenges, particularly for the millions of Americans impacted, with women bearing a disproportionate burden.
Caregivers often find themselves caught in a relentless cycle of adapting to the changing needs of their loved ones, which can lead to significant emotional and physical stress. With the number of individuals living with Alzheimer’s expected to rise, understanding the stages of the disease and the corresponding caregiving strategies becomes crucial.
This article explores the intricacies of Alzheimer’s, offering insights into its effects on caregivers and practical approaches to enhance the quality of care and support for both patients and their families.
We’re here for you, and together, we can navigate this journey.
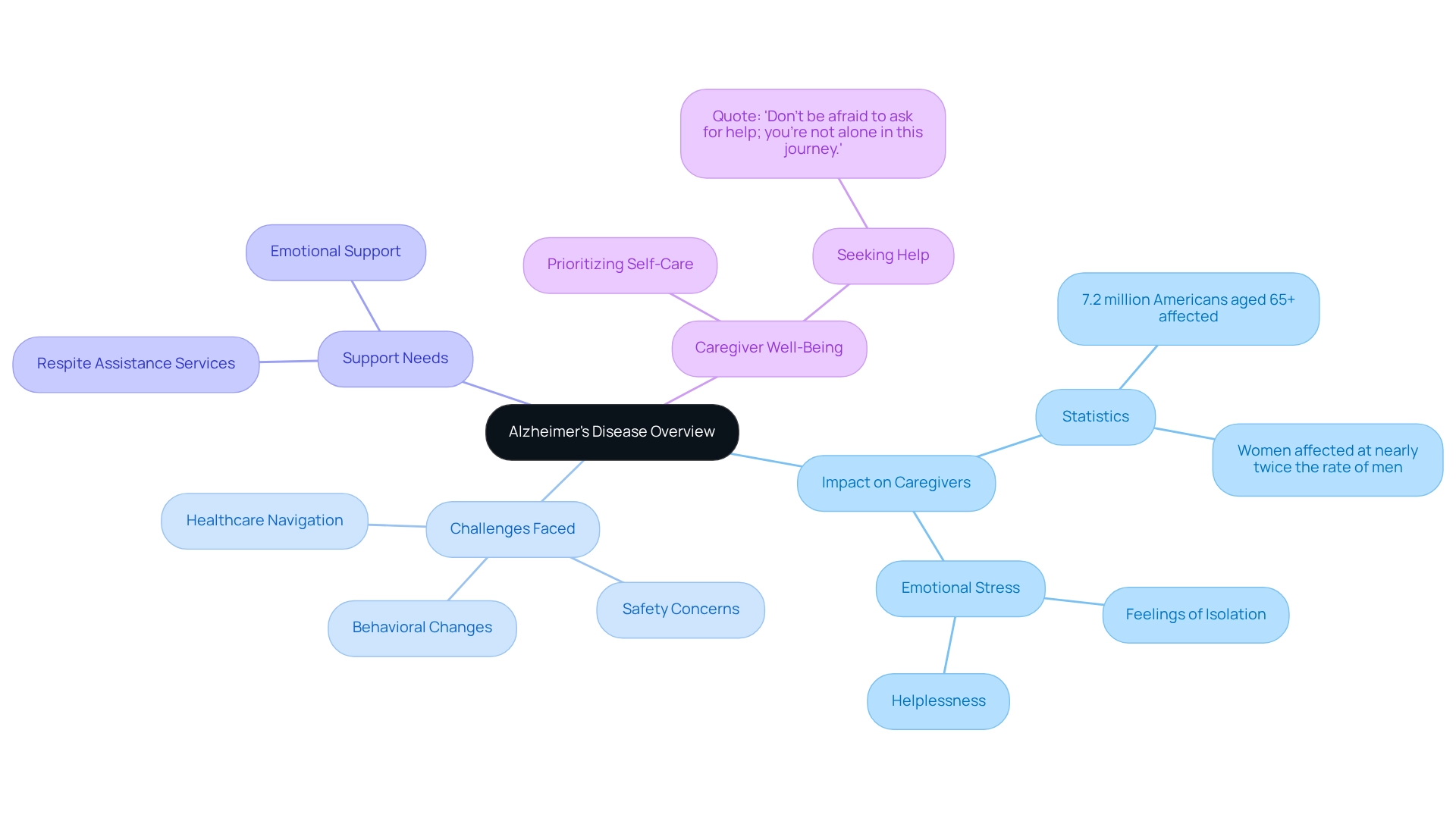
Overview of Alzheimer’s Disease and Its Impact on Caregiving
This form of dementia is a progressive neurological condition that greatly affects memory, cognition, and behavior, rendering it the primary cause of dementia. As of 2025, around 7.2 million Americans aged 65 and older are living with this condition, with women affected at nearly twice the rate of men. This disparity not only highlights the prevalence of the disease but also emphasizes the unique challenges encountered by women providing care, who often experience heightened stress levels due to their responsibilities.
The support journey for individuals with dementia is filled with obstacles. Caregivers must continually adjust to the changing needs of their family members, which can cause significant emotional and physical strain, frequently leading to health problems for those providing care.
Recent statistics suggest that individuals looking after Alzheimer’s patients experience higher levels of stress compared to those tending to people with other conditions. The emotional burden is significant, as those providing support often struggle with feelings of isolation and helplessness. Expert opinions emphasize the importance of seeking support. One healthcare professional notes, “Don’t be afraid to ask for help; you’re not alone in this journey.” This feeling underscores the importance for caregivers to prioritize their well-being while offering compassionate assistance. Cherishing moments with loved ones and recognizing the need for assistance can significantly improve the caregiving experience.
Best Care Nurses Registry provides tailored respite assistance services that address the specific requirements of families managing dementia. Our in-home caregiver services offer flexibility, companionship, and personalized assistance, ensuring that both the patient and caregiver obtain the help they require.
Case studies demonstrate that the influence of dementia reaches beyond the person diagnosed; it deeply impacts the whole family unit. Caregivers often face challenges such as managing behavioral changes, ensuring safety, and navigating the complexities of healthcare systems. With decades of experience, Best Care Nurses Registry has built a strong reputation in the home health care sector, providing essential support to families navigating these challenges.
As the prevalence of dementia continues to rise, understanding the 7 stages of Alzheimer’s and the associated caregiving demands becomes crucial for maintaining both the caregiver’s and the patient’s quality of life. By nurturing a supportive atmosphere and promoting open dialogue, families can more effectively manage the emotional terrain of dementia caregiving.
The Seven Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Comprehensive Breakdown
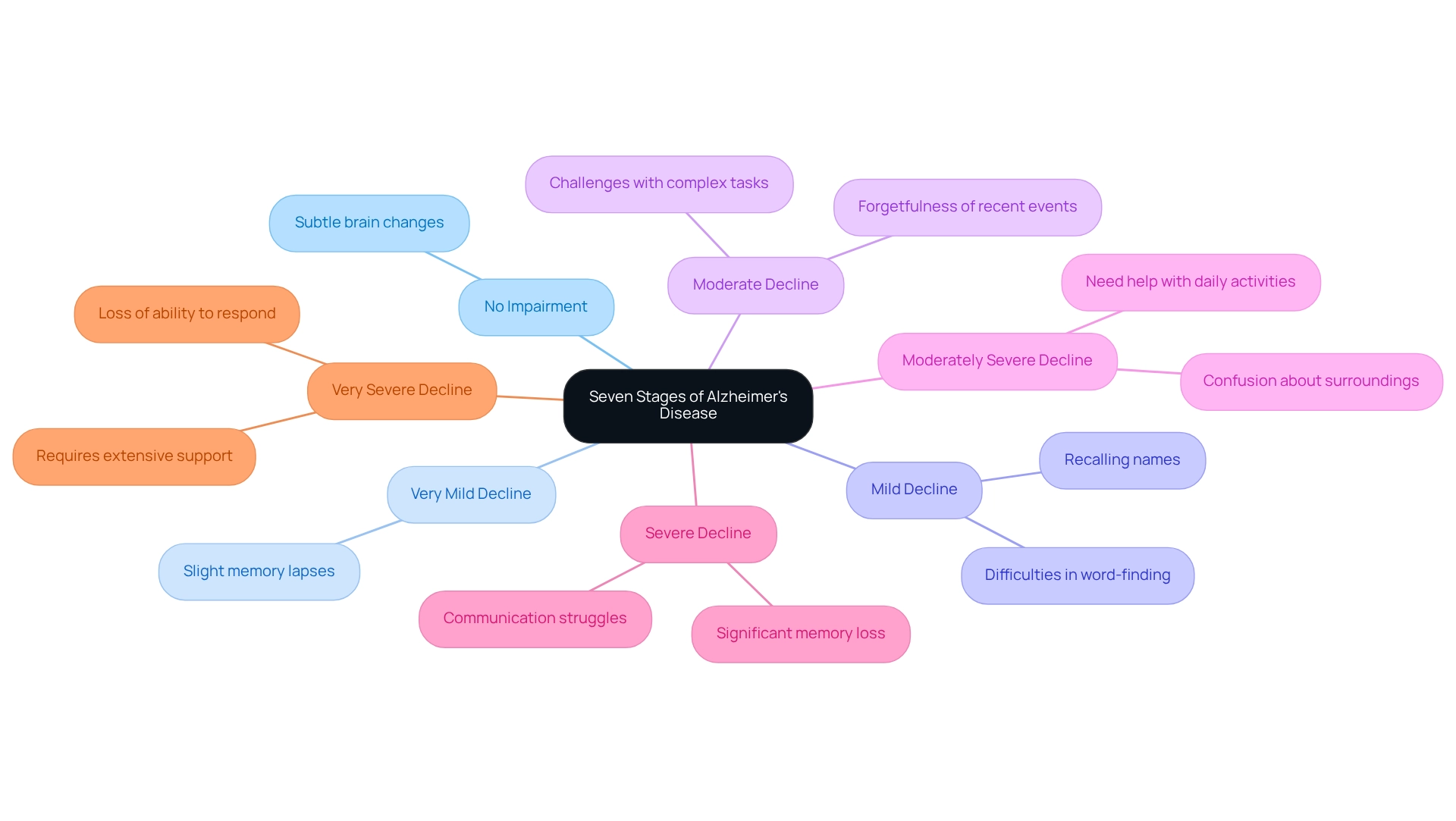
Alzheimer’s disease progresses through the 7 stages of Alzheimer’s, each characterized by specific symptoms and challenges that evolve over time.
- No Impairment: Individuals may show no noticeable symptoms, yet subtle changes in the brain are already taking place.
- Very Mild Decline: You might notice slight memory lapses, often dismissed as typical signs of aging.
- Mild Decline: Friends and family may begin to observe difficulties in word-finding or recalling names, indicating early cognitive changes.
- Moderate Decline: Clear symptoms of cognitive decline emerge, such as forgetfulness of recent events and challenges with complex tasks.
- Moderately Severe Decline: Individuals often need help with daily activities and may feel confused about their surroundings.
- Severe Decline: Significant memory loss becomes prevalent, and communication struggles can impact their ability to connect with others.
- Very Severe Decline: In this final stage, individuals lose the ability to respond to their environment and require extensive support for all daily activities.
Recognizing these phases is vital for supporters, as it allows them to adapt their assistance methods to meet the changing needs of their loved ones. Key signs indicating the need for CNA/HHA support services include difficulties with personal hygiene, dressing, cooking, and managing medications, which often become apparent as dementia progresses. Alarmingly, statistics show that more individuals are passing away at home, increasing from 15% to 37%. This highlights the urgent need for caregivers to understand the progression of dementia to provide effective home support.
Furthermore, the CDC reports that among individuals aged 70, 61% of those with dementia are expected to pass away before reaching 80, compared to 30% of those without the condition. This stark statistic underscores the severity of Alzheimer’s and the critical importance of proactive care. Additionally, studies reveal that 51% of individuals caring for those with dementia have never consulted a healthcare professional about navigating the complexities of the healthcare system. This emphasizes the need for enhanced support and education for caregivers, as understanding the 7 stages of Alzheimer’s and the associated symptoms and challenges can help them provide more compassionate and effective assistance. Best Care Nurses Registry offers tailored support options that alleviate stress for families seeking home health services, ensuring that caregivers are well-equipped to help their loved ones through every phase of dementia. Insights from the case study ‘Caregiver Assistance and Resource Utilization’ indicate that improving access to culturally appropriate resources and education about available support services can enhance the well-being of caregivers and the quality of care provided.
Caregiving Strategies for Each Stage: Adapting to Changing Needs
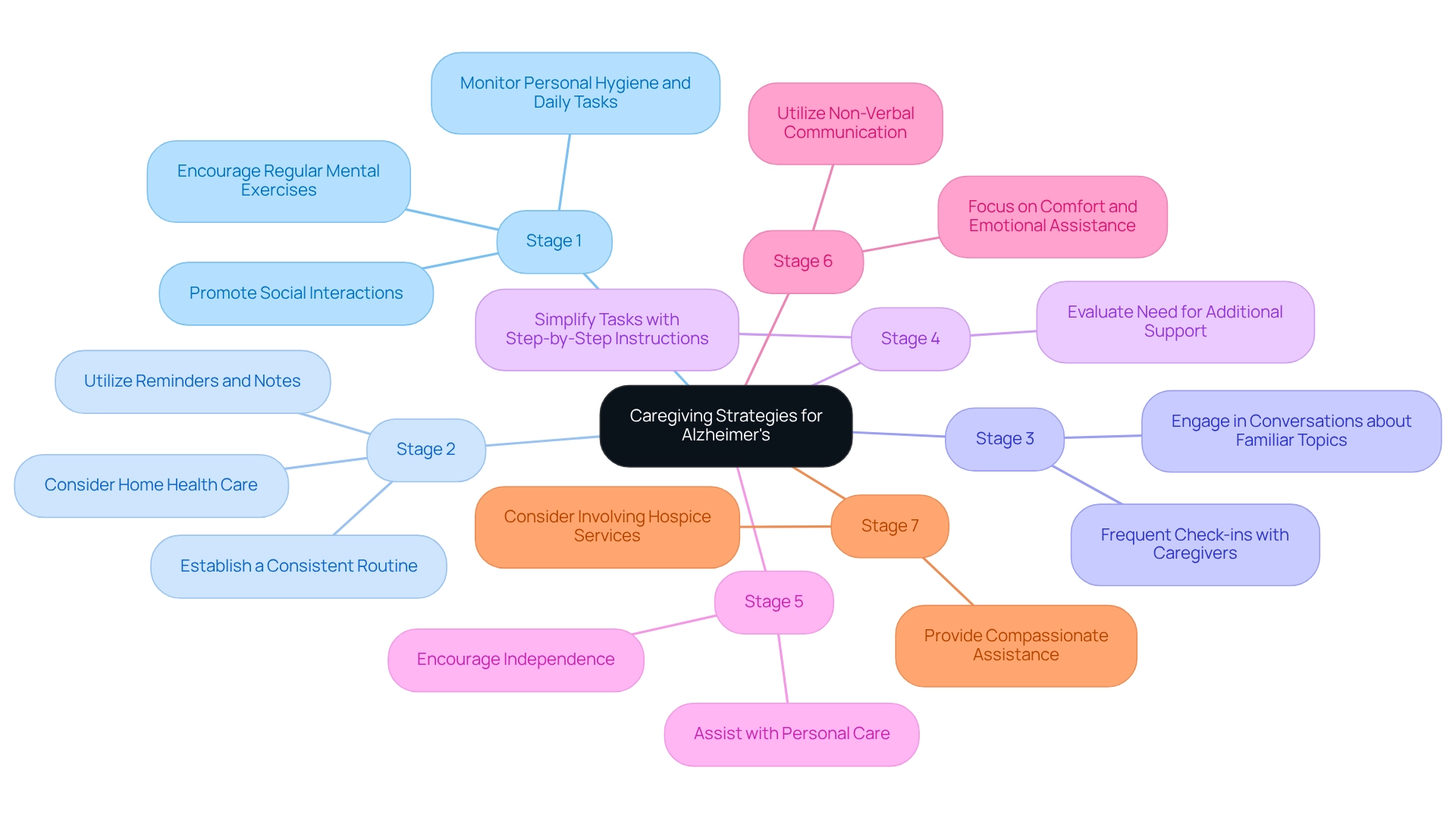
Adjusting caregiving approaches to the specific requirements of each of the 7 stages of Alzheimer’s is essential for providing effective assistance and improving the quality of life for patients. It’s important to recognize when to request CNA/HHA support services, as this can significantly influence the level of assistance offered.
- Stage 1: At this early stage, encourage regular mental exercises and social interactions to promote cognitive health. Engaging early can help maintain brain function. Observe any challenges with personal hygiene, dressing, cooking, cleaning, or managing medications to evaluate the need for assistance.
- Stage 2: Utilize reminders and notes to assist with memory lapses. Establishing a consistent routine can provide the necessary structure to ease anxiety. If memory issues escalate, consider the benefits of home health care, which is often more convenient and effective than institutional care.
- Stage 3: Engage in conversations about familiar topics to stimulate memory and offer reassurance, fostering a sense of connection and comfort. Frequent check-ins with caregivers can help ensure that your loved one receives the emotional support they require.
- Stage 4: Simplify tasks and provide step-by-step instructions to assist with daily activities, reducing frustration and promoting independence. This is a critical time to evaluate if additional support from a CNA or HHA is necessary to maintain safety and dignity.
- Stage 5: Offer assistance with personal care while encouraging independence where possible, ensuring safety without compromising dignity. The providers referred by Best Care Nurses Registry are trained to deliver this balance effectively.
- Stage 6: Focus on comfort and emotional assistance; non-verbal communication and familiar music can be powerful tools for connection during this stage. Maintaining transparent dialogue with those who provide assistance can enhance the standard of support given.
- Stage 7: Provide compassionate assistance that ensures comfort and dignity, and consider involving hospice services to support both the patient and family during this challenging time. Understanding the specific needs at each of the 7 stages of Alzheimer’s enables supporters to enhance their loved ones’ quality of life while managing their own stress and emotional well-being. Notably, impairment in one additional self-care activity for dementia patients can lead to an increase of 28 additional hours of family care required per month, underscoring the importance of effective caregiving strategies tailored to the 7 stages of Alzheimer’s. Moreover, the typical per-person Medicare expenditures for beneficiaries with Alzheimer’s or other dementias highlight the financial repercussions of providing care. The forthcoming GUIDE Model, which will incorporate education and support services for caregivers starting July 2024, offers additional resources for families. As emphasized by the Lancet Commission, technology is not a substitute for human contact, reinforcing the necessity for personal interaction in caregiving. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has raised concerns about its potential long-term effects on dementia prevalence, making it essential for caregivers to adapt their strategies in response to these evolving challenges.
Conclusion
Understanding Alzheimer’s disease and its profound impact on both patients and caregivers is essential for navigating this challenging journey. This article highlights the multifaceted nature of caregiving, emphasizing the emotional and physical toll on caregivers, particularly women who often shoulder a disproportionate burden. As the disease progresses through its seven stages, each marked by distinct challenges, caregivers must adapt their strategies to ensure the best possible support for their loved ones.
Recognizing the specific needs at each stage is vital. By employing tailored caregiving strategies, caregivers can enhance the quality of life for individuals with Alzheimer’s while also safeguarding their own well-being. Seeking support and utilizing resources such as respite care can alleviate stress and foster a more compassionate caregiving environment. Remember, caregivers are not alone; there are tools, services, and communities ready to provide assistance.
As the prevalence of Alzheimer’s continues to rise, promoting awareness and education surrounding the disease becomes increasingly important. By fostering open communication and understanding the progression of Alzheimer’s, families can better navigate the emotional landscape of caregiving. Together, with the right knowledge and support, caregivers can face the challenges of Alzheimer’s with resilience, ensuring that both they and their loved ones receive the care and compassion they deserve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Alzheimer’s disease and how prevalent is it among older Americans?
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological condition that significantly affects memory, cognition, and behavior, making it the primary cause of dementia. As of 2025, approximately 7.2 million Americans aged 65 and older are expected to be living with this condition, with women affected at nearly twice the rate of men.
What challenges do caregivers face when supporting individuals with dementia?
Caregivers often encounter numerous obstacles, including the need to continually adjust to the changing needs of their family members. This can lead to significant emotional and physical strain, resulting in health problems for the caregivers themselves.
How does the stress level of caregivers for Alzheimer’s patients compare to those caring for individuals with other conditions?
Statistics indicate that caregivers looking after Alzheimer’s patients experience higher levels of stress compared to those caring for individuals with other health conditions.
What emotional struggles do caregivers of dementia patients commonly face?
Caregivers often struggle with feelings of isolation and helplessness, highlighting the emotional burden associated with their responsibilities.
What advice do experts give to caregivers regarding seeking support?
Experts emphasize the importance of seeking support, encouraging caregivers to ask for help and reminding them that they are not alone in their journey.
What services does Best Care Nurses Registry offer to assist families managing dementia?
Best Care Nurses Registry provides tailored respite assistance services, including in-home caregiver services that offer flexibility, companionship, and personalized support for both the patient and caregiver.
How does dementia impact the entire family unit?
The influence of dementia extends beyond the diagnosed individual, deeply impacting the entire family. Caregivers face challenges such as managing behavioral changes, ensuring safety, and navigating complex healthcare systems.
Why is it important to understand the stages of Alzheimer’s and the associated caregiving demands?
Understanding the 7 stages of Alzheimer’s and the caregiving demands is crucial for maintaining the quality of life for both caregivers and patients as the prevalence of dementia continues to rise.
How can families effectively manage the emotional challenges of dementia caregiving?
By nurturing a supportive atmosphere and promoting open dialogue, families can more effectively navigate the emotional terrain of dementia caregiving.











